Erp-crm-software – ERP-CRM software: It’s the ultimate business power couple, seamlessly blending Enterprise Resource Planning and Customer Relationship Management. Imagine a world where your sales team knows exactly what’s in stock, your marketing campaigns target the *right* customers, and customer service is proactive, not reactive. That’s the promise of integrated ERP-CRM, a system designed to streamline operations and boost profits – and we’re diving deep into how it all works.
This isn’t just another tech explainer; we’re peeling back the layers to reveal the practical applications, the potential pitfalls, and the strategies for maximizing your ROI. From choosing the right deployment model to navigating the complexities of integration, we’ll equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions and unlock the true power of a unified system.
Integration Aspects of ERP-CRM: Erp-crm-software
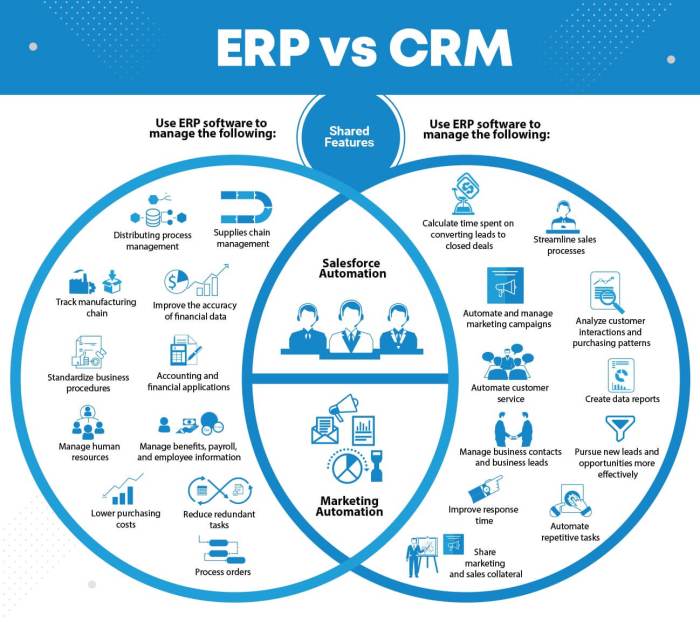
Integrating Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems can be a game-changer for businesses, streamlining operations and offering a unified view of customers and processes. However, this integration isn’t always a smooth ride. Successfully merging these powerful systems requires careful planning and execution to reap the full benefits.
ERP and CRM systems, while individually powerful, often operate in silos, leading to data inconsistency and inefficiencies. The challenge lies in bridging this gap, ensuring seamless data flow between systems without compromising data integrity or operational efficiency. A poorly executed integration can lead to more problems than it solves, resulting in wasted resources and frustrated employees. The key is a strategic approach that prioritizes data consistency, automation, and user experience.
Challenges of Integrating ERP and CRM Systems
Data discrepancies between systems represent a significant hurdle. Inconsistent data formats, differing data structures, and the lack of a standardized data model can lead to inaccuracies and inconsistencies across the organization. Furthermore, legacy systems often lack the flexibility needed for seamless integration with modern CRM platforms. The cost of integration, encompassing software, hardware, consulting, and internal resources, can be substantial. Finally, the complexity of the integration process itself can be daunting, requiring specialized expertise and careful project management. A lack of proper planning and understanding of the intricacies of both systems can easily lead to integration failure.
Best Practices for Successful ERP-CRM Integration, Erp-crm-software
A phased approach to integration, starting with a pilot project involving a limited scope, is crucial. This allows for testing and refinement before a full-scale rollout. Thorough data mapping and cleansing are essential to ensure data consistency and accuracy. Identifying and resolving data conflicts before integration begins is vital for success. The selection of the right integration tools and technologies is critical, and choosing a method that aligns with the organization’s technical infrastructure and expertise is essential. Robust testing and validation procedures are paramount to ensure the integrated system functions as expected and meets business requirements. Finally, comprehensive training for users is crucial for successful adoption and optimal utilization of the integrated system. This training should focus on the new workflows and functionalities enabled by the integration.
Approaches to ERP-CRM Integration
Cloud-based integration offers scalability, flexibility, and reduced infrastructure costs. Data is stored and managed in the cloud, accessible from anywhere with an internet connection. This approach simplifies maintenance and updates, but relies on a stable internet connection and requires careful consideration of data security and privacy. On-premise integration involves installing and managing the integration software within the organization’s own infrastructure. This offers greater control over data and security but requires significant upfront investment in hardware and software, as well as ongoing maintenance and support. A hybrid approach combines elements of both cloud-based and on-premise integration, offering a balance between flexibility, control, and cost. This approach allows organizations to leverage the benefits of both environments, tailoring the solution to their specific needs and resources.
Data Flow Between ERP and CRM Modules
Imagine a flowchart with two main boxes representing the ERP and CRM systems. Arrows connect these boxes. From the ERP side, arrows flow to the CRM, showing the transfer of data such as customer orders, invoices, and payment information. Simultaneously, arrows flow from the CRM to the ERP, representing data like customer interactions, sales opportunities, and marketing campaign results. Within each system, smaller boxes depict modules like sales, finance, inventory, and customer service. The arrows indicate the specific data flow between these modules. For instance, a customer order (ERP) updates customer information (CRM), and CRM lead conversion updates sales figures (ERP). This visual representation highlights the cyclical nature of data exchange, illustrating the dynamic interaction between the two systems. The clarity of this data flow ensures consistency and accuracy, preventing data silos and enhancing operational efficiency.
Deployment and Implementation
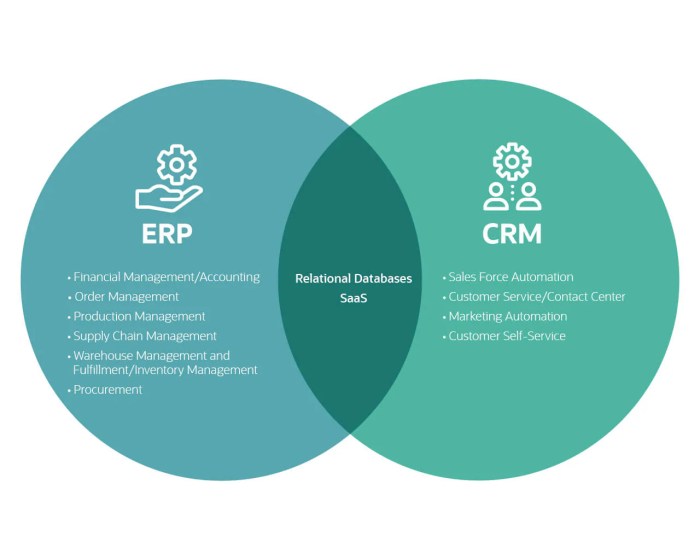
Choosing the right deployment model and executing a smooth implementation are crucial for the success of your ERP-CRM system. A poorly planned deployment can lead to significant delays, cost overruns, and user frustration, ultimately undermining the benefits of the system. This section explores the key considerations involved in deploying and implementing an ERP-CRM system, highlighting the differences between cloud and on-premise solutions and outlining potential pitfalls.
Cloud-Based vs. On-Premise Deployment
Cloud-based and on-premise deployments represent distinct approaches to hosting and managing your ERP-CRM software. Cloud-based deployments leverage a third-party provider’s infrastructure, offering scalability, accessibility, and reduced upfront costs. On-premise deployments, on the other hand, involve installing and managing the software on your own servers, granting greater control but requiring significant investment in hardware, software licenses, and IT personnel. The optimal choice depends on factors such as budget, IT infrastructure, security requirements, and the level of customization needed. For instance, a small business with limited IT resources might find a cloud-based solution more practical, while a large enterprise with stringent security protocols might prefer an on-premise deployment.
Steps Involved in Implementing an ERP-CRM System
Implementing an ERP-CRM system is a multi-stage process requiring careful planning and execution. The typical steps include: 1) Needs Assessment and Planning: Defining business requirements, selecting the right software, and creating a detailed implementation plan. 2) Data Migration: Transferring existing data from legacy systems to the new ERP-CRM system, ensuring data integrity and accuracy. This often involves cleansing and transforming data to fit the new system’s structure. 3) System Configuration and Customization: Tailoring the system to meet specific business needs, configuring workflows, and setting up user roles and permissions. 4) Testing and Training: Thoroughly testing the system to identify and resolve any bugs or issues before going live, and providing comprehensive training to end-users. 5) Go-Live and Post-Implementation Support: Launching the system and providing ongoing support and maintenance to ensure smooth operation. 6) Ongoing Optimization: Continuously monitoring system performance and making adjustments as needed to maximize efficiency and effectiveness. Each step requires meticulous attention to detail and effective collaboration between IT teams, business users, and vendors.
Potential Risks and Challenges During Implementation
ERP-CRM implementation projects often face various challenges. Data migration issues, inadequate user training, insufficient testing, and integration problems can cause delays and disruptions. Resistance to change from employees accustomed to existing systems is another common hurdle. Lack of clear communication and collaboration between different teams can also lead to conflicts and delays. Furthermore, cost overruns and scope creep are potential risks if the project is not carefully managed. For example, unforeseen complexities during data migration can significantly increase project timelines and costs. Effective risk management strategies, including detailed planning, thorough testing, and proactive communication, are essential for mitigating these challenges.
Comparison of Deployment Methods
| Feature | Cloud-Based | On-Premise |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lower upfront cost, subscription-based fees | High upfront cost for hardware and software licenses |
| Scalability | Highly scalable, easily adaptable to changing needs | Limited scalability, requires significant investment for upgrades |
| Maintenance | Vendor handles maintenance and updates | Requires dedicated IT staff for maintenance and updates |
| Security | Relies on vendor’s security measures | Greater control over security, but requires significant investment in security infrastructure |
Ultimately, ERP-CRM software is more than just a collection of tools; it’s a strategic investment that can transform your business. By understanding the core functionalities, mastering the integration process, and prioritizing user adoption, you can unlock significant efficiency gains, improve customer relationships, and drive sustainable growth. So, ditch the siloed systems and embrace the power of integration – your bottom line will thank you.
 Playfest Berita Teknologi Terbaru
Playfest Berita Teknologi Terbaru