Fast charging qualcomm quick charge 1 0 – Fast charging Qualcomm Quick Charge 1.0: Remember when waiting for your phone to charge felt like an eternity? Before the days of warp speeds and ridiculously fast charging, there was Quick Charge 1.0. This groundbreaking technology, a pioneer in the fast-charging revolution, marked a significant leap forward in mobile convenience. Let’s dive into the history, tech specs, and lasting impact of this charging OG.
This deep dive explores the technical details, compatibility issues, advantages, and disadvantages of Quick Charge 1.0, putting it in the context of the mobile landscape of its time. We’ll compare it to other charging methods available back then and see how it paved the way for the super-fast charging we enjoy today.
History and Evolution of Qualcomm Quick Charge 1.0: Fast Charging Qualcomm Quick Charge 1 0
Qualcomm’s Quick Charge technology revolutionized smartphone charging, moving away from the slow trickle charge that was the norm. Quick Charge 1.0, the pioneer of this revolution, laid the groundwork for the rapid charging speeds we enjoy today. Let’s delve into its history and see how far we’ve come.
Quick Charge 1.0 Launch and Key Features
Quick Charge 1.0 officially debuted in 2012, a time when charging a smartphone often felt like an eternity. Its key feature was the ability to significantly increase charging power compared to standard USB charging. This was achieved by using higher voltages, pushing more power into the battery in a shorter amount of time. While the exact voltage and current specifications varied depending on the implementation, the core principle was a marked increase in power delivery compared to the standard 5V USB charging prevalent at the time. This meant faster charging times, a welcome change for many users.
Comparison to Contemporary Charging Technologies, Fast charging qualcomm quick charge 1 0
In 2012, the smartphone charging landscape was a relatively barren one in terms of fast charging. Most phones relied on the standard USB charging protocol, delivering a maximum of 5V at a relatively low amperage, resulting in slow charging speeds. Quick Charge 1.0, while not as fast as later iterations, represented a substantial leap forward. It offered a noticeably faster charging experience compared to the standard charging methods available then, though still a far cry from the speeds seen in modern Quick Charge technologies. Competing technologies were mostly absent or less impactful in terms of widespread adoption.
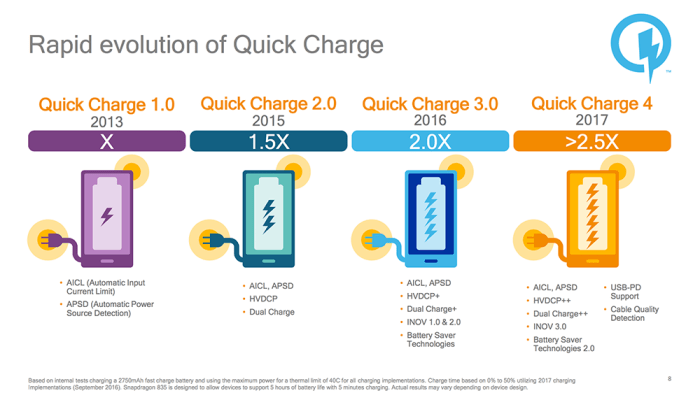
Timeline of Qualcomm Quick Charge Advancements
The evolution of Qualcomm Quick Charge has been a continuous race for faster charging.
| Version | Approximate Release Date | Voltage (V) | Current (A) | Power (W) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quick Charge 1.0 | 2012 | 5-9 | ~2 | ~18 |
| Quick Charge 2.0 | 2014 | 5-12 | ~3 | ~36 |
| Quick Charge 3.0 | 2015 | 3.6-20 | Variable | ~100 |
| Quick Charge 4.0 | 2017 | 3.6-20 | Variable | ~180 |
Note: The voltage and current values are approximate ranges, as the actual values depend on the device and charger implementation. Power is calculated as Voltage x Current.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Qualcomm Quick Charge 1.0

Qualcomm Quick Charge 1.0, while a groundbreaking technology in its time, wasn’t without its quirks. Let’s delve into the benefits it offered and the limitations it faced, comparing it to its contemporaries to paint a clearer picture of its place in fast-charging history.
Benefits of Quick Charge 1.0
Quick Charge 1.0 represented a significant leap forward in mobile charging speeds. Before its arrival, charging times were significantly longer, often taking hours to fully replenish a phone’s battery. The technology’s primary advantage was a noticeable reduction in charging time compared to standard charging methods. This was achieved through increased voltage and current delivery to the battery, allowing for a faster energy transfer. This translated to a tangible improvement in user experience, saving valuable time and eliminating the frustration of slow charging. For example, a phone that might take several hours to fully charge using a standard 5W charger could see a considerable reduction in charging time, perhaps reaching 50% charge in significantly less time. The convenience factor alone was a huge selling point.
Limitations of Quick Charge 1.0
Despite its advancements, Quick Charge 1.0 had its drawbacks. The higher voltage and current used to achieve faster charging resulted in increased heat generation within the device and the charger itself. This heat could potentially damage the battery over time, reducing its lifespan and overall performance. Furthermore, compatibility was limited to devices and chargers specifically designed to support Quick Charge 1.0, limiting its widespread adoption. The technology also lacked the sophisticated power management features found in later iterations of Quick Charge, potentially leading to less efficient charging in certain scenarios. The charging speed itself, while faster than standard charging, paled in comparison to later fast-charging technologies.
Comparison to Contemporary Technologies
Compared to other fast-charging technologies available around the same time (such as some proprietary solutions from different manufacturers), Quick Charge 1.0 offered a standardized approach, making it more accessible across different device brands – at least, those that chose to adopt it. However, its charging speeds were often slower and less efficient than some of the proprietary solutions that focused on specific device optimization. These proprietary systems, while not as widely adopted, sometimes managed to achieve faster charging speeds due to their tighter integration with the hardware. The lack of sophisticated power management in Quick Charge 1.0 also put it at a disadvantage compared to later iterations of the technology and other evolving fast-charging standards.
Summary of Advantages and Disadvantages
| Feature | Advantage | Disadvantage | Comparison to Alternatives |
|---|---|---|---|
| Charging Speed | Significantly faster than standard charging. | Slower than some contemporary proprietary solutions and later Quick Charge iterations. | Faster than standard, slower than some competitors. |
| Heat Generation | N/A | Increased heat production, potentially damaging battery longevity. | Similar issues in some competitors, but later technologies improved heat management. |
| Compatibility | Offered a standardized approach. | Limited to devices and chargers explicitly supporting Quick Charge 1.0. | More standardized than many proprietary solutions, but less widespread adoption than later standards. |
| Efficiency | Improved charging times. | Less efficient power management compared to later technologies. | Improved efficiency seen in subsequent Quick Charge versions and other fast-charging standards. |
Qualcomm’s Quick Charge 1.0, despite its age, holds a significant place in mobile history. It wasn’t just about faster charging; it was about changing expectations. While its speeds might seem glacial by today’s standards, it laid the groundwork for the rapid advancements we see in fast charging technology. It showed the world what was possible, setting the stage for the ultra-fast charging solutions we take for granted now. The legacy of Quick Charge 1.0 isn’t just about its specs; it’s about the revolution it ignited.
 Playfest Berita Teknologi Terbaru
Playfest Berita Teknologi Terbaru